We have started learning about LIVING THINGS.

What are living things?
Living things VITAL FUNCTIONS :
NUTRITION, REPRODUCTION and INTERACTION.
NUTRITION, REPRODUCTION and INTERACTION.
NUTRITION
Living things need water, food and air in order to grow.
They transform nutrients into energy in order to live.
Animal nutrition
-Carnivores: animals that eat only meat
-Herbivores: animals that eat only plants
-Omnivores: animals that eat both, plants and meat.
Plant nutrition
Plants absorve water and nutrients from the soil through
the roots.
This is called RAW SAP. On the leaves through the process of
photosynthesis, the raw sap changes into ELABORATED SAP.
They transform nutrients into energy in order to live.
Animal nutrition
-Carnivores: animals that eat only meat
-Herbivores: animals that eat only plants
-Omnivores: animals that eat both, plants and meat.
Plant nutrition
Plants absorve water and nutrients from the soil through
the roots.
This is called RAW SAP. On the leaves through the process of
photosynthesis, the raw sap changes into ELABORATED SAP.
REPRODUCTION
Living things can reproduce ASEXUALY or SEXUALY.
- In asexual reproduction, only one organism is required, for
example the bacteria.
- In sexual reproduction, two different types of individuals are
required: male and female.
This sexual reproduction can be:
-Viviparous: they are born from the mother's womb
-Oviparous: they are born from an egg
-Ovoviviparous: they are born from an egg inside the
mother's womb.
This sexual reproduction can be:
-Viviparous: they are born from the mother's womb
-Oviparous: they are born from an egg
-Ovoviviparous: they are born from an egg inside the
mother's womb.
INTERACTION
This is the relationship that living things have with the rest
of the world around it.
The five senses are part of this relationship: some living things
relate through the smell, othes through the sight, others
through the contact or touch, others through the taste or
others through the hearing.
of the world around it.
The five senses are part of this relationship: some living things
relate through the smell, othes through the sight, others
through the contact or touch, others through the taste or
others through the hearing.
What are cells?
The CELL is the basic unit of life.
There are two types of cells: animal cells and plant cells.
You will learn about the animal cell in this video.
You will learn about the animal cell in this video.
Here are some common parts of the cells.

Watch this video to see the differences between an animal
cell and a plant cell.
cell and a plant cell.
Remember that:
The NUCLEUS controls the functions of the cell.
The CELL MEMBRANE controls what enters and leaves the cell. The CYTOPLASM is a jelly-like substance in the cell where
chemical reactions happen.
The VACUOLES contain water and minerals, which the
organism needs in order to grow.
A strong CELL WALL protects the plant cell and gives it its
shape.
The CHLOROPLASTS in the plant cell contain chlorophyll
needed during photosynthesis.
TYPES OF ORGANISMS:
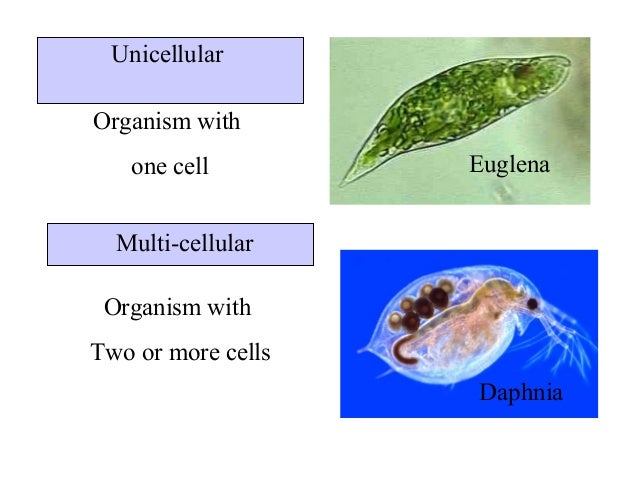
Organisms can be UNICELLULAR if they have only one cell .
MULTICELLULAR if they have many cells.
- Unicellular organisms are: most protists such as the amoeba
and some algae, bacteria and some fungi such as yeasts.
- Multicellular organisms are: animals, plants and some fungi
such as mushrooms and some protists such as some algae.
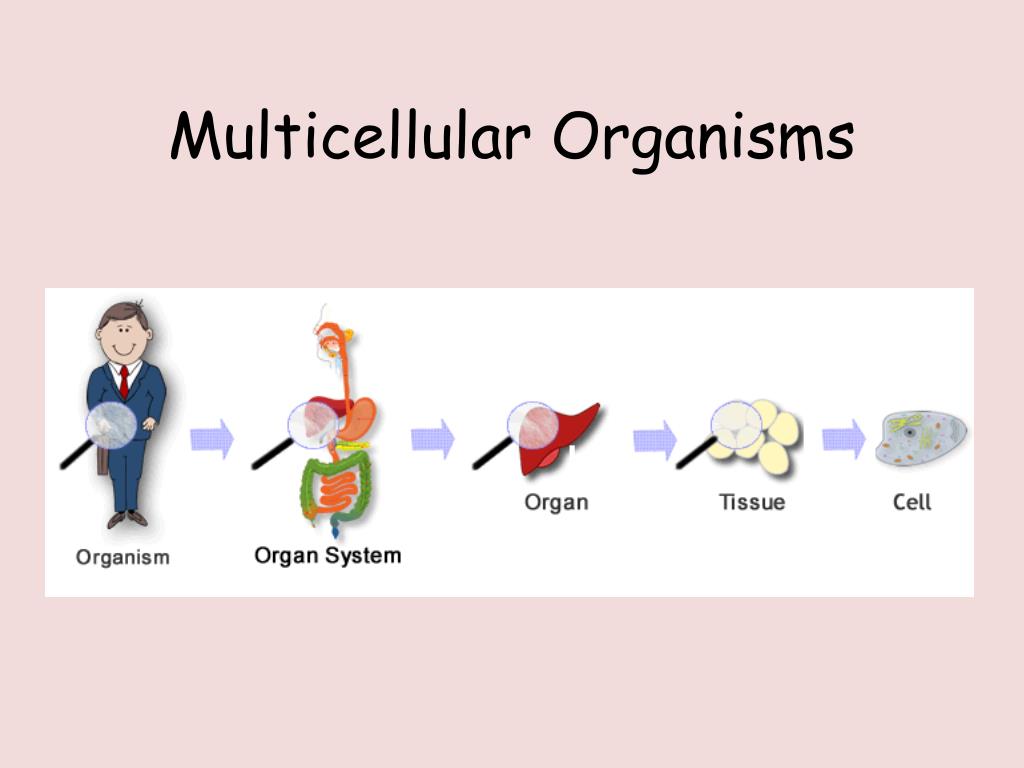
Watch this video to remember the different between cells, tissues,
organs and systems.
Remember the functions of the cells that we have learnt:
- The red blood cells carry oxygen.
- The white blood cells protect the body from bacteria, viruses
and other foreign invaders.
- The nerve cells carry nerve impulses from our brain to the rest
of the body and also from our sense organs to our brain.
- The root cells absorb water and minerals.
- The leaf cells collect sunlight for photosynthesis.
Remember that there are 5 KINGDOMS of living things:
- Plant kingdom: here we gather all types of plants.
Gymnosperm or not flowering plants.
Angyosperm or flowering plants
Gymnosperm or not flowering plants.
Angyosperm or flowering plants
- Protist kingdom: Protozoans, algae, and slime molds.
Many protists are so small that cannot be seen but with
a microscope.
Examples: amoeba and algae
Many protists are so small that cannot be seen but with
a microscope.
Examples: amoeba and algae
- Monera kingdom: a kingdom formed by unicellular
organisms. Bacterias.
organisms. Bacterias.
- Animal kingdom: here we gather all the types of animals.
Vertebrate animals with a backbone. They are subdivided
in Mammals, fish, reptiles, amphibians and birds
Invertebrate animals, without a backbone. They are
subdivide in: rthropods, molluscs, echinoderms, annelids, ....
Vertebrate animals with a backbone. They are subdivided
in Mammals, fish, reptiles, amphibians and birds
Invertebrate animals, without a backbone. They are
subdivide in: rthropods, molluscs, echinoderms, annelids, ....
- Fungus kingdom: Earth including on land, in the water,
in the air, and even in plants and animals. They cannot
make their own food so they feed from dead plants and
animals.
For example: Yeast, mushrooms
in the air, and even in plants and animals. They cannot
make their own food so they feed from dead plants and
animals.
For example: Yeast, mushrooms
Here you have a song about the five kingdoms.


Comments
Post a Comment